Prairie Goldenrod Seeds - Native Wildflower (Solidago ptarmicoides) for Late Summer Gardens
Regular price$4.00
/
Tax included.
4 reviews
Description
🌻 Experience the Golden Beauty of Prairie Goldenrod
Discover the stunning charm of Solidago ptarmicoides, a spectacular native perennial that creates masses of bright golden-yellow flower clusters from late summer through fall. This hardy prairie wildflower brings vibrant color when most other flowers are fading, making it an essential component of sustainable gardens and wildlife habitats.
✨ Key Features:
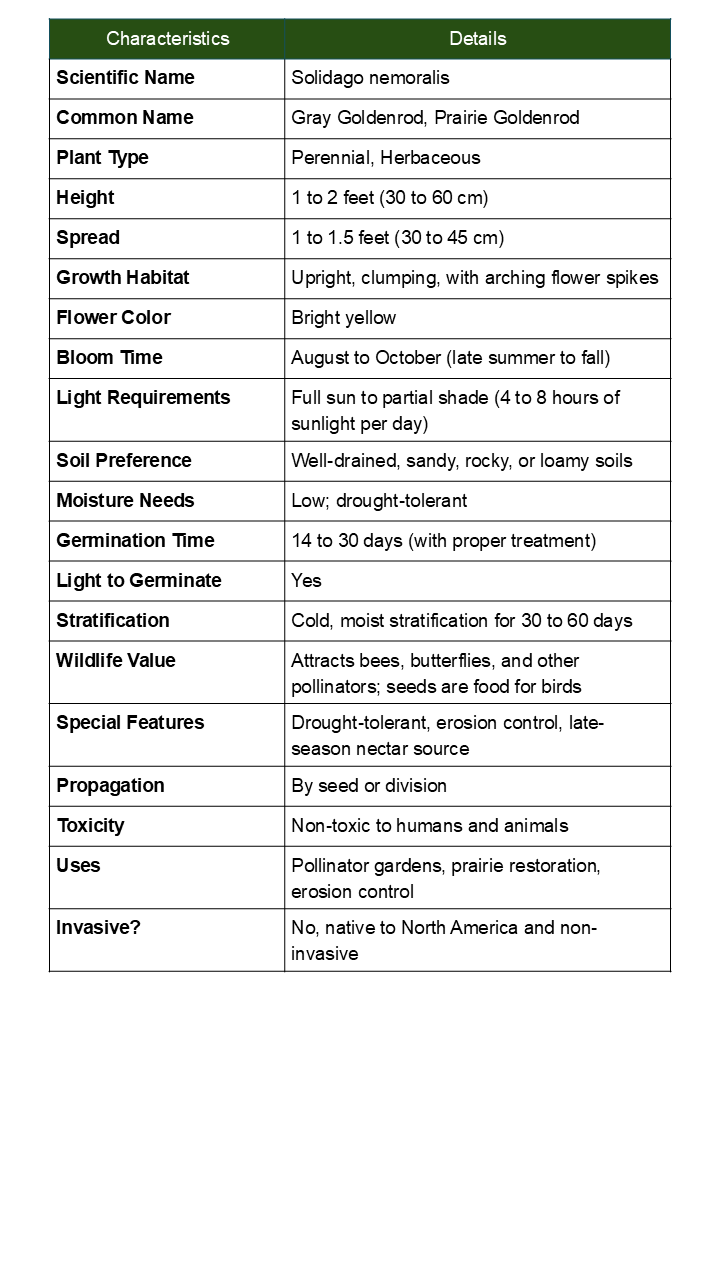
- Height: 1-3 feet tall with spreading, clumping habit
- Bloom Time: August through October (late season blooming)
- Flower Color: Bright golden-yellow in dense, fluffy clusters
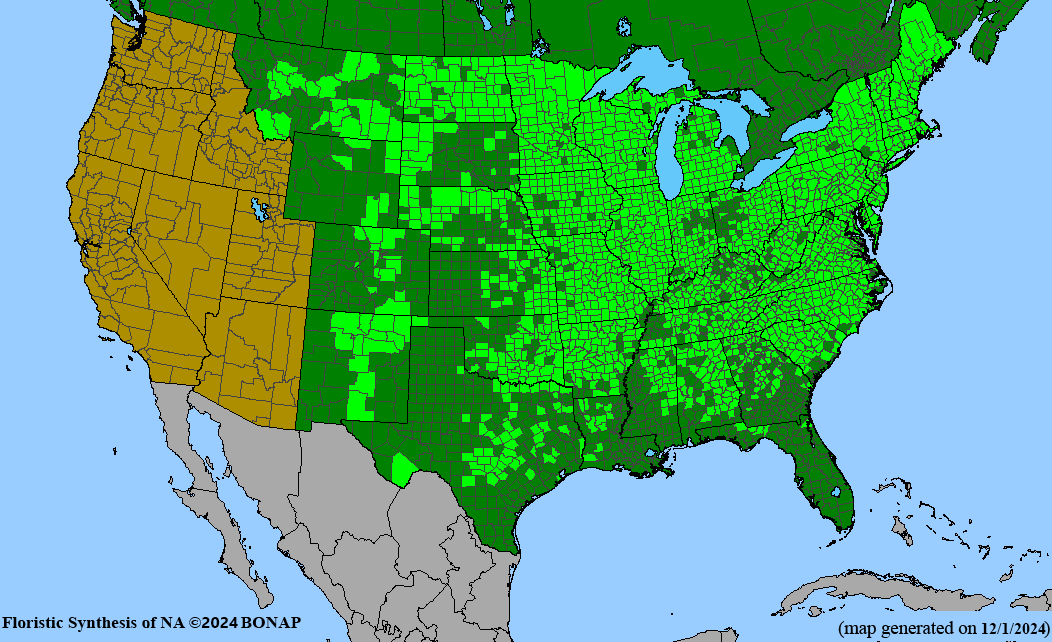
- Native Range: Central and Eastern North America
- Hardiness: USDA Zones 3-9
- Sun Requirements: Full sun to partial shade
🦋 Outstanding Wildlife Benefits:
- Critical late-season nectar source for migrating monarch butterflies
- Attracts over 100 species of native bees, butterflies, and beneficial insects
- Seeds provide essential winter food for goldfinches and other songbirds
- Supports declining pollinator populations when they need it most
- Long-lasting blooms extend pollinator season into autumn
🌱 Easy Growing Guide:
- Soil: Adaptable to various soils, tolerates poor and dry conditions
- Drought Tolerance: Excellent once established
- Maintenance: Low maintenance, may spread by rhizomes
- Germination: Cold stratification recommended for 30-60 days
- Spacing: Plant 12-18 inches apart for natural colonies
🏡 Garden Uses:
Perfect for prairie restorations, naturalized areas, pollinator gardens, and fall displays. Creates stunning golden drifts and provides crucial habitat for wildlife.
Create spectacular late-season displays while supporting migrating butterflies and native ecosystems. This essential prairie native brings both beauty and critical ecological value to sustainable gardens.