Whorled Milkweed Seeds - Native Asclepias Verticillata | Monarch Butterfly Host Plant
Rare Native Whorled Milkweed - Monarch Butterfly Essential
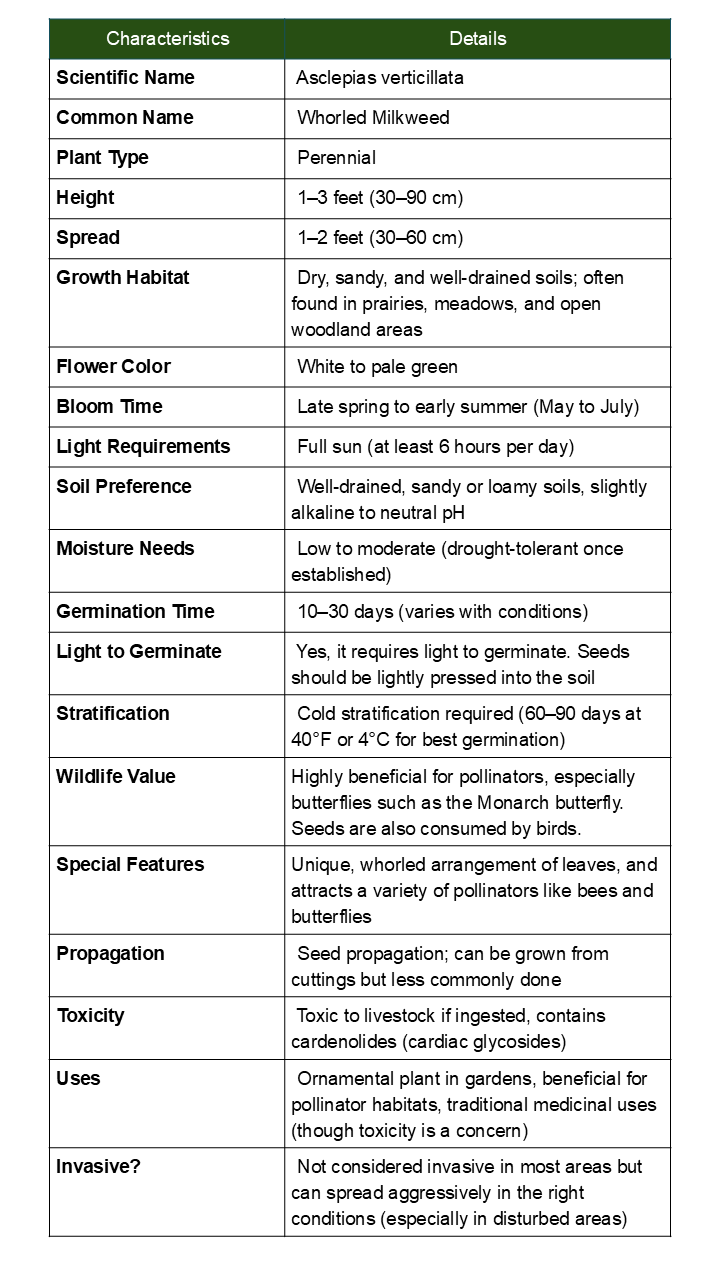
Asclepias verticillata, commonly known as Whorled Milkweed or Horsetail Milkweed, is a unique and delicate native perennial that brings essential monarch butterfly habitat to your garden. This distinctive milkweed features narrow, needle-like leaves arranged in whorls around the stem, creating an elegant, fine-textured appearance. Small clusters of greenish-white flowers bloom from summer through fall, providing crucial nectar for monarchs and other pollinators when they need it most.
Distinctive Features:
- Monarch Butterfly Host: Essential breeding plant for monarch caterpillars and nectar source for adults
- Unique Foliage: Narrow, whorled leaves create fine texture unlike other milkweeds
- Drought Champion: Extremely drought tolerant once established with deep root system
- Extended Blooming: Flowers continuously from summer through fall
- Compact Size: Perfect for smaller gardens and naturalized areas
Growing Information:
Height: 1-3 feet | Spread: 1-2 feet | Sun: Full sun to partial shade | Soil: Well-draining, adaptable to poor soils | Zones: 3-9
Planting Guide: Direct sow in fall or cold stratify seeds for 30 days before spring planting. Seeds need light to germinate - barely cover with soil. Extremely drought tolerant and thrives in sandy, rocky soils.
Create a vital monarch waystation while enjoying the unique beauty of this rare milkweed that supports declining monarch populations with its distinctive fine-textured foliage and reliable nectar source.
SHIPPING WITHIN USA